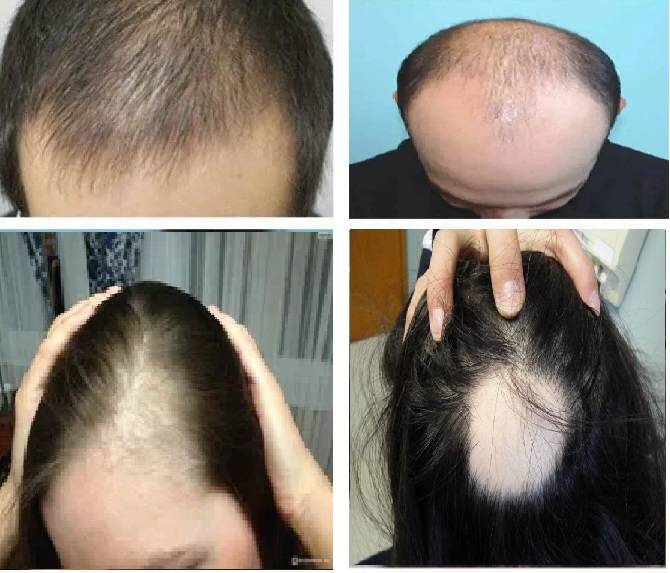
Female hair loss is usually diagnosed when a person loses an unexpectedly large amount of hair. Naturally, we all lose 50 to 100 hairs per day. Hair loss is part of the natural cycle of hair growth; Old hair falls out to make room for new hair. When the balance between new hair growth and old hair loss is disturbed, we face the problem of hair loss or baldness. Excessive hair loss is called alopecia or baldness in medical science.
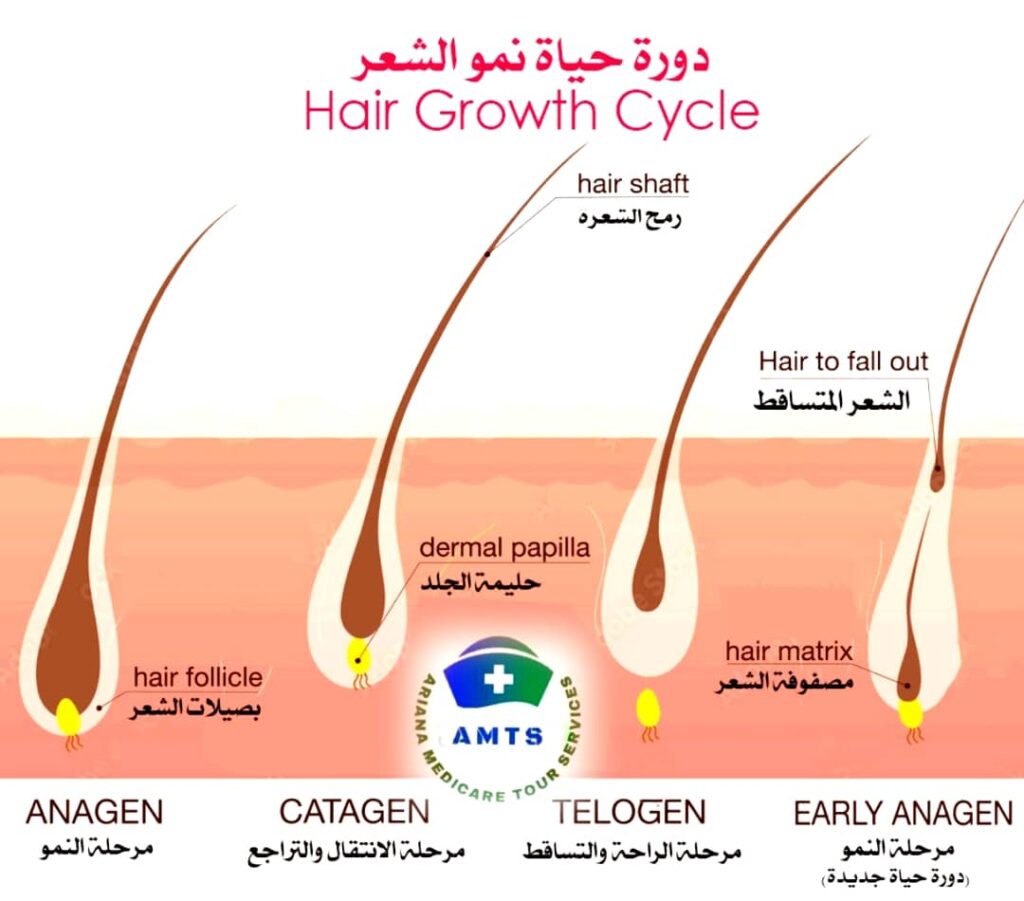
The hair and body hair growth cycle naturally has three phases:
Anagen (Growth Phase) This stage lasts between 2 and 8 years. Naturally, 85 to 90% of our head hair is in this phase.
Catagen phase (transient phase): This phase lasts 2 to 3 weeks and the follicles degenerate.
Telogen phase (resting phase): This phase lasts from two to four months, at the end of which hair falls out.
How common is hair loss in women?
Who suffers from hair loss?
Any girl or woman may experience shedding; But this problem is more common in the following people:
Women over 40 years old
Women who have recently given birth.
Women undergoing chemotherapy or taking other special medicines.
Women who have a habit of tying their hair tightly or braiding it.
Women who constantly use harmful chemicals for their hair.
Causes of hair loss in women:
The causes of hair loss in men and women vary. For ease of action, we’ve put these causes into 4 categories: alopecia areata, lifestyle, clinical causes and hormonal changes. The causes of hair loss in women can be seen alone or in combination.
Since hair loss can be caused by a serious underlying disease, we recommend that you consult your doctor if you are suffering from this problem.
1. Alopecia areata:

Alopecia is a form of hair loss that is not contagious and can have various causes. From genetic causes to tight hair ties or anything that further stimulates your immune system.
Androgenic alopecia:
Female pattern hair loss or androgenetic alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss in women, and it is genetically caused. Meaning, if someone in your family has androgenetic alopecia, you are most likely to have it.
Androgenic alopecia becomes more severe due to the decrease in the amount of estrogen during menopause, the causes of which we examined a little earlier. You should know that less than 50% of women reach the age of 65 with a hairline and the rest suffer from this type of hair loss.
How does androgenic alopecia appear?
Androgenetic alopecia in men causes patchy baldness. But in women, what we often see is a decrease in overall hair density and hair thinning. In general, androgenetic alopecia in women has three stages or states:
The first step: reduce the density of hair on both sides of the parting line
The second stage: expanding the lower back
Stage III: specific baldness in the line of separation with lumbar sections
What is the cause of genetic baldness?
The main cause of androgenetic alopecia is heredity. If your father, mother or other close relatives suffer from this type of baldness, the possibility that you will also suffer from it increases.
Underlying diseases and tumors can also cause female pattern baldness. If you are experiencing symptoms such as irregular menstruation, severe acne, increased hair growth with hair loss, be sure to see a doctor.
Smoking is also associated with an increased incidence or severity of the disease.
Most people with androgenetic alopecia experience significant hair loss between the ages of 40 and 50.
Can female pattern hair loss be treated?
Hair transplantation for women
The only definitive treatment for androgenetic alopecia in men is hair transplantation. But in women, hair transplantation is usually a bit difficult for this type of baldness. Because androgenic alopecia causes baldness in parts of the head and parts remain intact; Like the areas behind the head called hair banks. The follicles in the hair bank area in men are resistant to androgenic hormones and have a good density.
This condition does not exist in women. That is, the follicles of the hair bank are not resistant to loss, and because the hair loss is not concentrated and leads to a decrease in the density of all parts of the head, the hair bank cannot be used to fill in the density. Therefore, women with this type of alopecia may not be suitable candidates for transplantation.
Minoxidil for hair loss in women
It is a topical medication sold in the form of 2% and 5% solutions and foam in pharmacies. This drug has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat female pattern baldness. Minoxidil should be applied to your scalp daily. It takes about 4 months to a year to see the effect of this medicine.
Minoxidil cannot completely replace hair loss; But to some extent, it causes the growth of new hair and increases its density. Usually, the shedding returns after stopping the medication.
Minoxidil side effects:skin redness
itchy
skin dryness
unwanted hair growth in some areas; Especially the cheeks area
Can hereditary hair loss be prevented?
No; To date, no method has been identified to prevent this complication. In general, eating healthy, not using harmful hair styles, curling irons and harmful chemicals, as well as quitting smoking, can delay the onset of hair loss or reduce its severity.
- Traction alopecia:
One of the most common causes of hair loss in women is tying or braiding hair in a way that stretches the hair. Tight ponytails, afros, and other tight weaves can cause hair to pull and pull. This type of hair loss is called traction alopecia. In this case, the hair follicles may be damaged and permanent baldness may occur.
- Alopecia areata:
Alopecia areata, is an autoimmune skin disease in which cells of the immune system attack and damage follicles. Alopecia areata is observed in the form of localized circular baldness. This type of baldness is usually temporary, but it may recur many times throughout life.
2. Life style
Food:
Improper diet and lack of certain nutrients can be one of the causes of hair loss in women. Hair loss caused by a nutritional deficiency is usually temporary and will grow back if you fix the problem. Let’s review these important points together:
A sharp decrease in calorie intake
On some diets, calorie restriction is very strict. Your hair needs energy to grow, which is provided by the calories in food. So if you get too little energy from food, the blood flow and nutrition to your scalp will decrease and you will experience hair loss.
Protein deficiency:
Almost all body structures are made up of proteins or proteins and amino acids are their main components. Hair is no exception to this rule and one of its main parts is a protein called keratin. For this reason, protein deficiency can also be one of the causes of hair loss in women
Vitamin deficiency:
Vitamins A, C, D and E are essential for the health of your skin and hair. Also, a vitamin from the B family of vitamins, called biotin, is an essential component in making hair keratin. An acute deficiency of these vitamins, which appears in rare cases, can be one of the causes of hair loss in women.
Iron and zinc:
Iron is one of the most important components of red blood cells. Red blood cells, with the help of iron, receive oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to the tissues of the body. If you have an iron deficiency (which is common in women), the oxygen supply to the follicles and scalp decreases and hair falls out.
Zinc is also essential for healthy skin and hair. The effect of zinc appears clearly in people with hypothyroidism. In these people, zinc deficiency is common, and by making up for it, hair loss also improves.
3. Clinical reasons
Severe shock and stress:
Physical and psychological trauma such as the loss of a family member, extreme weight loss, major surgeries, acute illnesses, and childbirth can cause temporary hair loss. This type of hair loss is called telogen effluvium. Indeed, due to stress, the hormonal balance in the body is disrupted, the natural hair cycle is disrupted, and more hair enters the telogen phase (hair loss phase).
Other stresses that can cause sudden hair loss:
High temperature
severe infection
chronic diseases
Serious physical injury such as the loss of a body part
Poisons:
Toxins such as chemotherapy, radioactive rays in radiotherapy, and the use of certain medications can disrupt the normal cycle of hair and cause telogen effluvium. Medications for blood pressure, arthritis, heart medications, and some other medications are also toxic to hair. Hair loss caused by these substances is usually temporary; But if the follicles are damaged, they become permanent.
In general, hair loss is a side effect of medications. If you have this problem, consult your doctor to stop or change your medication.
Underlying diseases:
One of the causes of hair loss in women is an underlying disease. In fact, baldness and hair loss can be symptoms of other diseases, some of which we have mentioned below:
Thyroid diseases: hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, Hashimoto’s disease
Hodgkins disease
Hypothyroidism
Addison’s disease
lupus
psoriasis
scleroderma
Celiac disease
infection such as ringworm (dermatophytosis)
These diseases can cause hair loss and baldness by imbalanced hormones, causing autoimmune problems and scarring.
4. Hormonal hair loss:
The relationship between hair loss and menopause
During menopause, one of two things may happen to your hair. First, hair may grow in areas where you had no hair before. Secondly, your hair may become thinner and fall out.
One of the reasons for this is that during menopause, the level of sex hormones in the body changes. The production of estrogen and progesterone (female hormones) decreases, and the effect of androgenic hormones (male hormones) such as testosterone on the follicles increases.
Estrogen maintains hair density, and androgen hormones cause hair loss and thinning. In addition to hormonal imbalance, other factors such as stress, diet, and genetic issues also contribute to hair loss and make it more severe.
** The relationship between hair loss, pregnancy and lactation:
Post-pregnancy hair loss is one of the most common causes of hair loss in women. Of course, this is completely normal and should not cause you to worry. During pregnancy, hormonal changes reduce hair loss and improve the quality of your hair.
About 3 months after giving birth, some mothers experience telogen effluvium. which we mentioned above. After childbirth (again due to hormonal changes) there is a temporary disruption in the hair growth cycle which leads to hair loss. This type of hair loss is temporary and new hair grows back very quickly and replaces the lost hair.
Because post-pregnancy hair loss occurs three months after giving birth, some people think it has something to do with breastfeeding. Hair loss after pregnancy is not related to breastfeeding and does not improve or worsen with stopping or continuing breastfeeding. So don’t worry about this either.
Sometimes other causes of hair loss in women coincide with hair loss after pregnancy. Consult your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Abnormal pattern of hair loss: For example, if your pattern of hair loss is similar to androgenetic alopecia or alopecia areata.
Pain or itching at the site of the spill
Redness or scaling of the scalp
Increased number of acne
Increased facial hair
irregular periods