The comprehensive guide on rheumatism and its treatment in Iran. In this article, we will learn about the causes and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and the various treatment options available. Iran has emerged as a leading destination for medical tourism, providing world-class facilities and experienced professionals in the field of rheumatology. So, let’s explore the world of rheumatology and discover its best treatments in Iran.
Introduction:
Joint rheumatism or rheumatoid arthritis causes joint pain and swelling, and its symptoms are weakness and chronic fatigue.
1- What is rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis?
2- Know the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
3- The cause of rheumatism and its treatment.
3.1- Factors that increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis.
3.2- What is the treatment of rheumatism with physiotherapy? From, a decrease in the range of motion of the joints and muscle strength. Physiotherapy methods can be used to treat joint rheumatism.
3.3- Medication treatment.
3.4- Platelet therapy
3.5- Exercise therapy.
3.6- Other treatments.
What is rheumatism or rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks its own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation, pain, and swelling in the joints of the body.
The inflammation causes the joints to become painful, hot, and swollen, and to have limited movement. Dry joints in the morning are also common. This disease is usually chronic and if left untreated, in the long term, the inflammation caused by rheumatism can damage the joints and cause their destruction.
The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. This cause is associated with a combination of hormonal, environmental, and hereditary or hereditary factors. One in every hundred people will be affected by this disease in their lifetime.
Joint rheumatism, especially knee rheumatism, has a higher prevalence in women, and women suffer from this disease three times more often than men. Joint rheumatism (rheumatoid arthritis) usually occurs between the ages of 35 and 60, but according to most research, the likelihood of developing rheumatoid arthritis is higher in middle age.
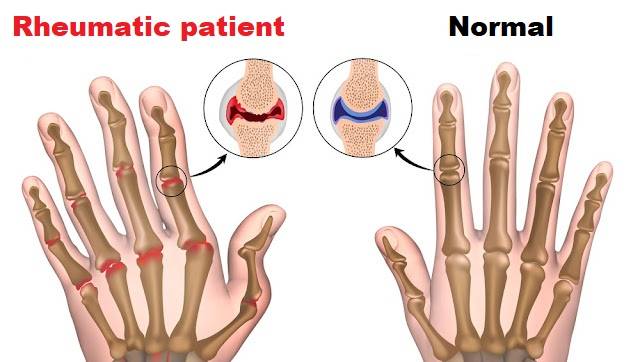
Learn about the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
The most common symptoms of rheumatism include:
- Swelling, pain and heat in the joints. The small joints of the hands or feet are usually affected.
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes (or joint stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes if you are at rest during the day).
- Decreased joint range of motion and muscle strength.
- Chronic weakness and fatigue.
- Abnormal sensation such as burning or shooting.
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain.
- muscle weakness
- Flu-like symptoms, such as feeling hot and sweating.
- headache.
- neck pain
- Anorexia.
- Fever.

The cause of rheumatism and its treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by the immune system attacking the inner layer of the joint membrane, or synovium (the layer of membranes around the joint). The usual role of the immune system is to protect us from infection.
However, when a person has an autoimmune disease, instead of attacking external factors such as an infection, the immune system attacks the healthy tissues of the body, thus causing inflammation and damage to the joints.
Swelling occurs when a joint produces too much synovial fluid in response to inflammation. Sometimes other parts of the body such as the lungs and eyes are affected. The resulting inflammation causes the synovial membrane to thicken and eventually to destroy the cartilage and bone within the joint.
The tendons and ligaments (ligaments) that hold joints together become weak and stretched, and the joint gradually loses its normal shape and order.
Factors that increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis.
Factors that increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Gender: Rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women than in men.
- Age: Rheumatoid arthritis can occur at any age, but it most commonly occurs between the ages of 35 and 60.
- Family history: If one family member has had rheumatoid arthritis, the chance that other family members will also be affected increases.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can be mild or severe depending on the stage of the disease. In this disease, when joints become inflamed and painful, range of motion and muscle strength decrease.
How is rheumatism treated with physical therapy?
One of the solutions that help reduce joint pain and dryness is the use of physiotherapy methods, and methods of treating joint rheumatism in physiotherapy include the use of electrotherapy to reduce pain and inflammation, massage, ultrasound, softening and stretching exercises, joint strengthening exercises, etc.
The purpose of physiotherapy is to reduce pain and increase flexibility, strength and joint movement to prevent dehydration and deformity of the joints as well as muscle weakness. Physiotherapy not only prevents the recurrence of pain, but also improves the general state of health
Medication treatment
The type of medication your doctor prescribes depends on the severity of your symptoms and the duration of your rheumatoid arthritis.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include ibuprofen and naproxen sodium. Stronger types of these medications require a doctor’s prescription.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and prevent permanent damage to joints and other tissues. Common medications in this class include methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine.
- Biological agents: Also known as biological response modifiers, these are the new generation of DMARDs. These medications can target the parts of the immune system that cause inflammation and joint and tissue damage. These types of medications increase the risk of infection.
Platelet (plasma) treatment for rheumatism [PRP].
Plasma injection [PRP] or platelet-rich plasma therapy is a treatment based on the body’s ability to heal. PRP treatment begins with taking a blood sample from the patient. The blood is spun in a centrifuge to obtain a platelet solution that contains a high concentration of growth factor proteins. The benefits of these proteins are:
- Pain relief.
- Accelerate and facilitate the wound healing period.
- Reconstruction and repair of soft body tissues.
- Using PRP to treat this type of arthritis facilitates the body’s natural healing process. Of course, PRP has other benefits for rheumatic patients. Because PRP injections use the patient’s own blood, there is no risk of infection. Additionally, PRP reduces recovery time compared to other treatments.
Therapeutic exercise therapy.
Exercise is beneficial for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and most patients are aware of this; But finding the time, energy, and motivation to exercise is hard. – It becomes difficult for the patient to exercise, especially if he is in pain. But research has shown that rheumatoid arthritis patients who exercise experience less pain than other patients. In addition, aerobic exercise boosts morale, improves joint function, and prevents muscle weakness and atrophy. In the following, we will provide exercises suitable for rheumatoid arthritis patients:
- Water sports.
- Walking.
- Bike riding.
Other treatments.
In addition to taking the medications mentioned, in some cases you need surgery, arthroscopy, or joint replacement to improve treatment, reduce symptoms, and recover faster. Arthroscopy is used to remove inflamed joint tissue.