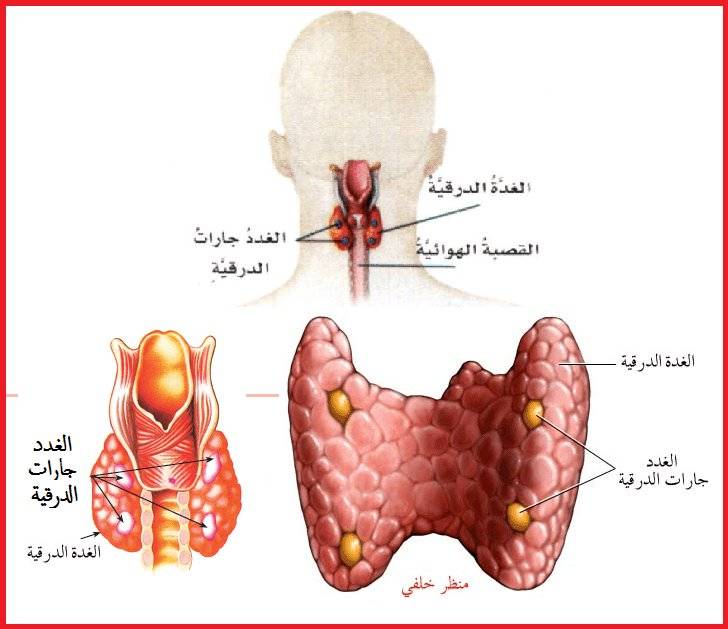
The thyroid gland is a small gland located in the front of the neck, and is part of the digestive system. The thyroid gland plays an important role in regulating the functions of the body, as it secretes the hormones thyroxine (T4) and thyronine (T3), which affect the metabolism, growth and development of the body.
Some people have thyroid problems, such as an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). These problems can be treated with medication or, in some cases, surgery.

Article contents
- Introduction
- Thyroid
- How does the thyroid gland work?
- Diseases and disorders of the thyroid gland
- Goiter
- Hyperthyroidism
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
- Diagnostic methods thyroid activity
- Methods of treating thyroid activity
- Insufficiency and lethargy of the thyroid gland
- Symptoms of lethargy and hypothyroidism
- Treatment of hypothyroidism
- Single thyroid nodule
- Thyroid cancer
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Hypothyroidism symptoms (Hashimoto’s)
- Methods for diagnosing the gland
- Thyroid (Hashimoto’s)
- Methods of treatment (Hashimoto’s)
- Thyroid gland in children and its treatment
- Hypothyroidism and its treatment in pregnant women
- Treating thyroid symptoms during pregnancy
- Types of thyroid treatments in Iran, Shiraz
- Nutrition for the treatment of thyroid gland
- The last word
Thyroid:
The thyroid gland is the largest gland in the neck. This gland is located in the front of the neck and under the layers of skin and neck muscles. The thyroid gland is in the shape of a butterfly with its wings (the right and left thyroid lobes) around the trachea. The specific function of the thyroid gland is to produce thyroid hormone. The field of influence of this hormone is in almost all tissues of the body, because this hormone increases their cellular activity, so the role of the thyroid gland is to regulate the body’s metabolism.
How does the thyroid gland work?
The thyroid gland is a small gland that usually weighs less than an ounce and is located at the front of your neck. This gland consists of two halves (lobes) that lie along the trachea and connect to a narrow strip of thyroid tissue (called the isthmus).
The function of the thyroid gland involves absorbing iodine (found in food) and converting it into thyroid hormones. These hormones are thyroxine (T4) and thyroiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body that can absorb iodine. These cells produce the T3 and T4 hormones by combining iodine with the amino acid tyrosine. These hormones then enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body in order to control the body’s metabolism (the conversion of oxygen and calories into energy).
The regulation of the metabolism of every cell in the body depends on thyroid hormones. A normal thyroid gland produces about 80% T4 and about 20% T3, however, the “strength” of T3 is about four times as strong as T4.
The thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland, a small, peanut-sized gland located at the base of the brain. When levels of the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) drop too low, the pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more of the hormone. Under the influence of TSH, the thyroid gland begins to produce and secrete T3 and T4 hormones, and as a result, the level of these hormones in the blood increases.
The pituitary gland is also regulated by another gland called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that produces the TSH releasing hormone (TRH). This hormone commands the pituitary gland to stimulate the thyroid gland (to secrete TSH). The hypothalamus can be likened to someone adjusting a thermostat because it tells the pituitary gland what level the thyroid gland should adjust to.
Diseases and disorders of the thyroid gland
Here are some of the more common disorders of thyroid disease:
- Goiter:
This complication is called the formation of a bulge in the neck. A toxic goiter is associated with an overactive thyroid gland. A nontoxic goiter, which is known as a simple or original goiter, is caused by an iodine deficiency. - Hyperthyroidism:
These complications occur due to an overproduction of thyroid hormone. People with hyperthyroidism are often sensitive to heat, hyperactivity, and overeating. Goiter is sometimes a side effect of hyperthyroidism. This condition occurs due to overstimulation of the thyroid gland and inflammation of the thyroid gland tissue.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism are: nervousness, increased heart rate, insomnia, premature suffering, body tremors, increased sweating, sleep problems, skin thinning, muscle weakness, brittle hair and nails, and puffiness under the eyes. with Graves’ disease.

Methods for diagnosing thyroid activity:
If a person goes to the doctor with these symptoms, the doctor will first write a test for them. The amount of thyroid hormones in the blood is determined by a blood test. High levels of these hormones mean that a person has an overactive thyroid gland. Another way to diagnose hyperthyroidism is for a doctor to inject some radioactive iodine into the human body orally or by injection, and then check the amount of iodine absorbed by the thyroid gland.

Ways to treat thyroid activity:
To treat this disorder, antithyroid medications such as Tapazole are used, which reduce the production of thyroid hormones. In some severe cases, it is necessary to surgically remove the thyroid gland, as the person suffers from hypothyroidism with this operation, and to compensate for the work of the thyroid gland, he must take thyroid hormone on a daily basis.
Hypothyroidism:
This complication is a common disease characterized by a severe decrease in thyroid hormone production. In infants, this condition is known as cretinism. Cretinine has very serious side effects, including abnormal bone growth and mental retardation. If you (as an adult) have hypothyroidism, you may have symptoms of sensitivity to cold, loss of appetite, lethargy, and general lethargy. Hypothyroidism often goes undiagnosed for years before it is medically diagnosed.
Symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland: feeling tired, depressed, dry skin, increased sensitivity to cold, memory problems, sudden weight gain, constipation, low heart rate, and in severe cases a person enters a coma!

Treatment of hypothyroidism:
It is the regular use of medications associated with this disorder. With regard to the treatment of this disorder, it is very important to pay attention to the dose received, because these pills increase the secretion of thyroid hormones, and taking them in abundance increases the possibility of symptoms of hyperthyroidism in a person.
Single thyroid nodule:
The formation of single nodules or masses in the thyroid gland is very common. It is estimated that more than half of the population has thyroid nodules. The majority of these nodules are benign. It is usually identified by fine needle biopsy (FNA) of the carcinoma nodule.
Thyroid cancer:
Thyroid cancer is relatively common, however, and patients have an excellent long-term survival rate. In some cases, symptoms such as hoarseness, neck pain, and swollen lymph nodes can occur in people with cancer. And the thyroid gland occurs. Cancer can affect anyone of any age, but it is more likely to affect women and people over the age of 30.
- Thyroiditis: This condition is called thyroiditis, which may be related to abnormal function of the thyroid gland (particularly hyperthyroidism). Inflammation can cause thyroid cells to die. As a result, the thyroid gland will not be able to produce enough hormones to maintain a normal metabolism in the body. There are five types of thyroiditis and each requires its own treatment.
Also this inflammation is called as “Hashimoto’s”. This disorder is also known as lymphocytic thyroiditis. This disorder in and of itself is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. This disease occurs in different age groups, but its prevalence is higher among middle-aged women. In this disease, a person’s immune system mistakenly identifies the thyroid gland as a foreign agent and attacks it. In this way, the body gradually destroys the thyroid gland. Simply put, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease where the body attacks the thyroid gland. Mild disease causes many thyroid symptoms not to appear. For this reason, it may be present in some people for several years and not be diagnosed because there are no symptoms.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism (Hashimoto's):
Feeling tired, depressed, thin and dry hair, constipation, slight weight gain, swollen and pale face, sensitivity to cold, dry face and skin, irregular menstruation, enlarged thyroid gland.
Methods for diagnosing hypothyroidism (Hashimoto's):
Testing is the first step to diagnosing this disorder. This disease is considered an autoimmune disease, and one of the most important symptoms for its diagnosis is the presence of abnormal antibodies that attack the thyroid gland.

Hashimoto's treatment methods:
Usually, to reduce the effects of this disease, medications are prescribed to compensate for the decreased production of thyroid hormones. In severe cases, all or part of the thyroid gland is surgically removed.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism in children in Iran:
To answer a question, it is necessary to clarify that hypothyroidism is very common among middle-aged women, however, it also appears in children.
Some children are born without a thyroid gland or their thyroid gland does not function properly, and these children also have their own symptoms, such as: umbilical hernia, loud and intense crying, difficulty breathing, large and protruding tongue, jaundice, and so on. The whites of the eyes and yellowing of the skin, due to the lack of production of a substance called bilirubin in the child’s body.
Gradually, as the disease progresses in children with thyroid disorders, the children face problems in the feeding process, and this may cause a disruption in the child’s growth and development. Children with thyroid disorders also have other symptoms, such as weak muscle contractions, excessive sleepiness, and constipation.
Taking care of thyroid symptoms in children is very important because neglecting these symptoms and not treating thyroid disorder can lead to mental and physical retardation of the child.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism and its treatment in pregnant women:
Thyroid hormones are essential for normal fetal development in the first trimester. Since there is a possibility of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism during pregnancy, the thyroid level should be controlled before conception and during pregnancy. Thyroid diseases are relatively common during pregnancy and it is important to check for thyroid symptoms and ways to treat them.
Note that thyroid hormones are particularly important for ensuring proper fetal brain and nervous system development during the first trimester of pregnancy, as the proper growth of your baby depends on the hormones moving across the placenta. At about 12 weeks, the thyroid gland in the fetus begins to produce its hormones.
If you already had hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism before you became pregnant, you should get extra medical attention, especially in the first trimester (to control these conditions during pregnancy).
Symptoms of hypothyroidism during pregnancy:
Sometimes, pregnancy itself may cause thyroid symptoms similar to hyperthyroidism. You should contact your doctor if you experience new or bothersome symptoms such as:
- Heart palpitations
- or lose weight
- or persistent vomiting.
Untreated thyroid disease during pregnancy may lead to the following symptoms:
- Premature birth
- Hypertension
- abortion
- Low birth weight.
Treating thyroid symptoms during pregnancy:
The severity of thyroid symptoms and their treatment during pregnancy also depends on the level of thyroid hormone in the blood.
- For women who need treatment for hyperthyroidism and thyroid symptoms, an antithyroid medication that blocks the production of thyroid hormones is used. This medication – propylthiouracil (PTU) – is usually prescribed in the first trimester of pregnancy, and if needed and diagnosed by a doctor, methimazole can be used after the first trimester.
Hypothyroidism is treated with a synthetic (man-made) hormone called levothyroxine, which is similar to the T4 hormone produced by the thyroid gland. The doctor adjusts the dose of levothyroxine during pregnancy and continues to monitor thyroid function tests (every 4 to 6 weeks) during pregnancy.
Diagnostic methods and techniques, types of examination and tests in thyroid diseases in Iran:
- Radiography:
Imaging In many cases, a look at the thyroid gland can answer many questions. Your doctor may perform an imaging test called a thyroid scan when you notice thyroid symptoms. This will allow him or her to check your thyroid gland and see if it is enlarged, forming, or growing (nodules). - Ultrasound:
Usually you don’t need to change your system Diet or fasting before ultrasound. During the test, you lie flat on an examination table with your head resting on a pillow so that your head is tilted back. A warm, water-soluble gel is applied to the skin of the area to be examined. - Physical examination:
Noting Your Thyroid Symptoms Another way to quickly check for thyroid symptoms is a physical examination in the clinic. This is a very simple and painless test in which the doctor feels at the front of your neck to detect any growths or enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid disease treatments in Iran.
Antithyroid drugs:
(Methimazole and Propylthiouracil): These are medications that prevent the thyroid gland from producing hormones.
Surgery:
A more permanent form of treatment. The doctor may surgically remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). This blocks the production of hormones.
There are two main ways to perform this surgery and remove the thyroid gland in Iran, in Shiraz:
- Through an incision in the front of the neck.
- Through an incision in the armpit and using an endoscope
Attention:
There are foods that are prohibited in hyperthyroidism
- Linum seed
- Lunar cabbage.
- Peanuts.
- cabbage.
- turnip.
- mustard.
- millet.
- cauliflower.
- yellow turnip.
- peach.
- coffee.
- spinach
- Eliminate simple carbohydrates and sugars:
A low-carb diet is recommended, which emphasizes complex carbohydrates and avoids simple sugars. According to the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University, foods with a high glycemic index (such as refined grain products and sugary drinks) may increase inflammation in the body.

last word:
In this article, the question of what are thyroid symptoms is answered and you learn more about thyroid treatment. Did you know that the thyroid gland is one of the most important glands in the body that produces important and vital hormones in the body. The increase and decrease in the production of these hormones has its own problems, and as soon as you notice the symptoms, it is best to see a doctor for thyroid treatment.
Iran, especially the city of Shiraz, is a pioneer in the treatment of thyroid diseases such as goiter.